【Sui Complete Review (Part 2)】Sui Move and Sui Move / PTB / Horizontal Scaling Technology / On-Chain Storage / Other Sui Technologies and Protocols for Users and Developers / @SuiNetwork
Continuing from yesterday, we will explain everything about Sui.
Good morning.
Mitsui from web3 researcher.
TodayKuripto Kuripto contributes an article.This article is the middle part of a series of three articles titled "Sui Complete Review".This article is the middle part.If you haven't seen it yet, please take a look at the first part, which was updated yesterday!
6. Move and Sui Move
7. PTB (Programmable Transaction Blocks)
8. Sui's Horizontal Scaling Technology
9. Sui's On-Chain Storage
10. Various Other Sui Technologies/Protocols
6. Move and Sui Move
Sui uses its own language called Sui Move, based on the Move language developed for Meta's Diem project Sui Move, this helps prevent the mishandling of resources.It is a programming language designed specifically for blockchain, specifically for the secure management and manipulation of digital assets.
The language has a powerful "type system," most notably the concept of "resource types" at its core, which makes digital assets and other valuable data unrepeatable and indestructible.It prevents unauthorized copying of tokens and other important assets, making them fundamentally more secure at the language level.In addition, Move is a statically typed language and is designed with type safety in mind, detecting many errors at compile time and minimizing run-time errors.
Another important feature of the Move language is its module-based code structure.Each module has independent functionality and only works with other modules through explicit interfaces.This facilitates code encapsulation and enhances security.Modularity facilitates continuous improvement and expansion of applications because it allows updating only specific parts.For example, when a new authentication system or upgrade is needed, partial updates can be made without having to shut down the entire system.
As an example, the following X post by Move language developer Sam Blacksear answers the question, "Is it possible to build zkLogin on Solana?"This is the answer to the question "Is it possible to build a zkLogin on Solana?
According to this post, in order to build zkLogin on Solana, the flexibility regarding Solana's authentication schemes will be important.I don't understand the details myself, but Sui is designed from the beginning to easily integrate new authentication schemes and other features, allowing for flexible updates and feature additions.In terms of application-level change requests, the flexible development environment of the Move language has worked positively to add such features to Sui on a regular basis.
If you would like to learn more about the Move language in more detail, please refer to this article written by Onigiri.
[Sui] Smart Contract Development - Move vs. Rust (Move language and its security).
[Sui] Smart Contract Development - Move vs. Rust (Solana vs. Move)
7. PTB (Programmable Transaction Blocks)
Sui Move's proprietary technology is PTB (Programmable Transaction Blocks), which plays a particularly important role in enhancing scalability.In traditional blockchain systems, transactions are limited to a single action, limiting the development of complex applications.
However, the PTB breaks this down and allows multiple actions to be combined into a single transaction.This allows developers to create sophisticated applications that can perform many operations in a single transaction.
Because PTB can consolidate up to 1024 transactions into a single block, it can efficiently handle large, complex tasks that have been difficult to process with previous blockchain systems.
For example, a large volume of NFT issuance or game application processing with multiple user actions, which previously would have required many individual transactions, can be combined into a single transaction using the PTB.This reduces network load and improves overall processing speed and efficiency.
In addition, the PTB has a transaction integrity assurance mechanism whereby the entire transaction is considered a failure unless all actions in the block succeed.This feature prevents errors and data inconsistencies due to partial processing, thus preserving the integrity of the blockchain.
With the introduction of PTB, Sui will be dramatically more scalable and efficient than traditional blockchains, allowing developers to create more diverse and sophisticated applications.
8. Sui's Horizontal Scaling Technology
While scaling solutions are being tried on various blockchains, the author believes that the horizontal scaling technology that Sui is working on implementing is the best solution to the scaling problems faced by general-purpose blockchains.
There are two main types of scaling: vertical scaling and horizontal scaling.Vertical scaling (scale-up) is a method of enhancing the performance of existing servers.
Specifically, hardware resources such as CPU, RAM, and storage are increased to allow a single machine to process more data and transactions.This approach is used in many systems because it is relatively simple to implement and easy to configure and manage systems.
However, there are physical limits to vertical scaling.There is an upper limit to server performance, and once that limit is exceeded, further expansion becomes difficult, thus limiting long-term scaling.In addition, raising the machine requirements for validators tends to raise the hurdle for network participation, making it difficult to ensure distribution.
Horizontal scaling (scale-out), on the other hand, is a method of expanding system processing capacity by distributing the load across multiple servers.
Adding new servers improves the overall system performance and can theoretically be scaled indefinitely.Horizontal scaling can be complex to implement because it utilizes techniques such as load balancing, data partitioning, and replication, but it provides high scalability and reliability.
Sui is attempting to address the scaling issues of blockchain by introducing horizontal scaling in place of traditional vertical scaling.
A new horizontal scaling technology called "Pilotfish" has already been demonstrated as of March 2024.According to the results of this experiment, Pilotfish has demonstrated a throughput improvement of up to 8x with 8 additional servers compared to a single server.This result demonstrates Pilotfish's ability to scale almost linearly with compute load.
8-1. Horizontal scaling mechanism with Pilotfish
8-1-1. Overview
Pilotfish is the first multi-machine smart contract execution engine that allows validators to use multiple machines to process transactions on the Sui blockchain.This technology is unique in that validators can easily deploy additional machines when the network load increases, allowing horizontal scaling of transaction processing capacity.
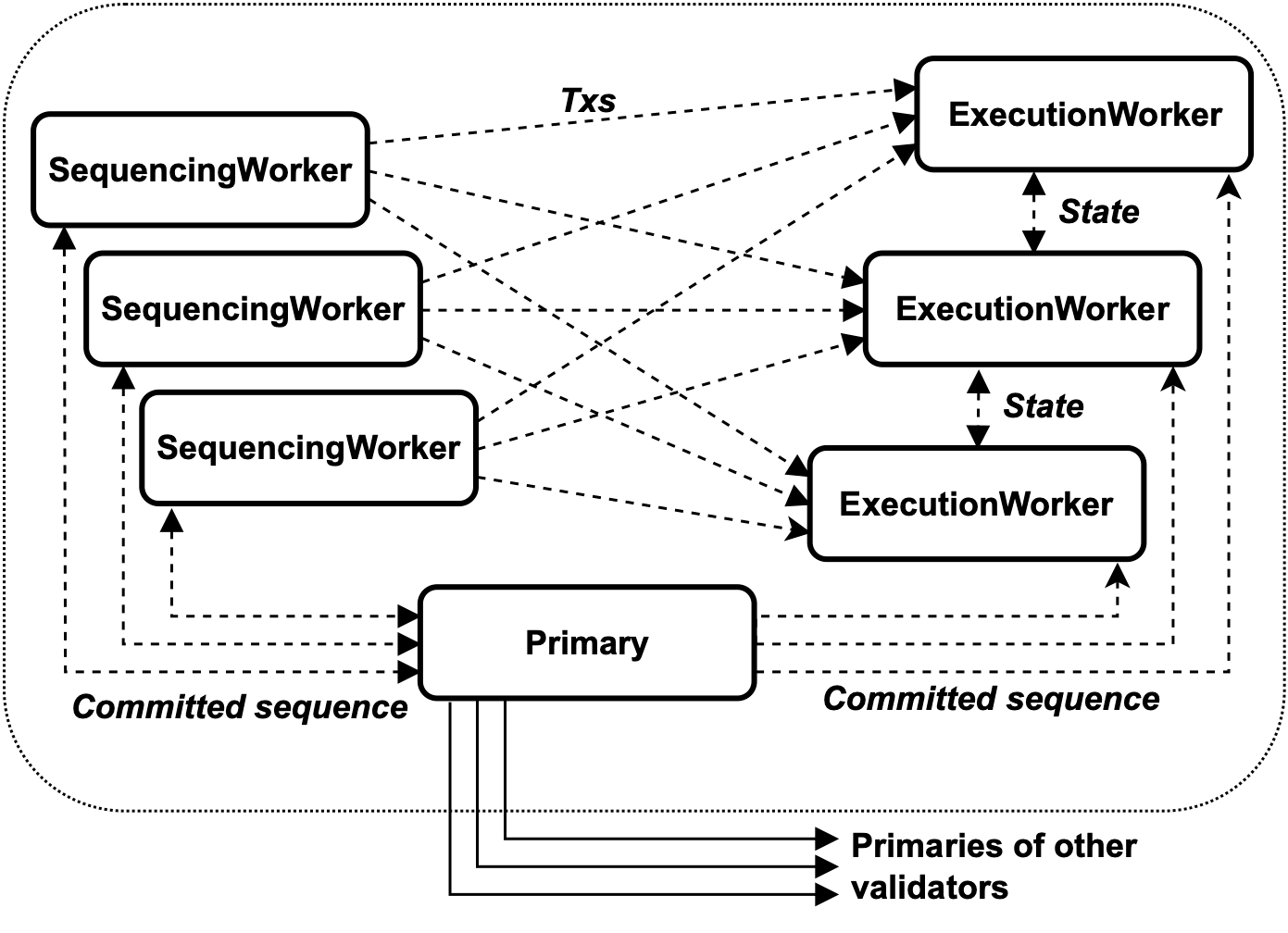
8-1-2. Basic Architecture
In Pilotfish, each validator is internally divided into three roles
Primary
Sequencing Workers (SW)
Execution Workers (EW)
The Primary is responsible for consensus across the network, the SW is responsible for sequencing transactions and their transmission, and the EW executes transactions and manages the state of the blockchain.EW then executes transactions and manages the state of the blockchain.
Pilotfish allows each of these roles to be distributed across multiple machines, thereby distributing the transaction processing load.Of particular importance is the fact that EWs and SWs use the concept of sharding to split and process data.This allows each EW to execute transactions independently and improves the scalability of the overall system.
8-1-3. Sharding and Transaction Processing
As explained in the previous section, EW and SW use sharding to divide and process transaction data.
Sharding is the art of dividing a database into smaller parts (shards), each of which is managed by a different server.Pilotfish incorporates a mechanism for exchanging necessary data between EWs when a transaction accesses data across multiple shards.
For example, if a transaction requires data from two different shards, it is first checked to see if the data is managed by different EWs, and then the transaction is executed once the necessary data is in place.This process maximizes the likelihood that transactions will be executed in parallel and improves overall processing speed.
8-1-4. Performance and Scalability
Pilotfish's effectiveness is particularly pronounced for computationally intensive transactions.
As noted above, experimental results from March showed that Pilotfish can improve throughput by up to a factor of 8 with 8 EWs compared to 1 EW.This result demonstrates Pilotfish's ability to scale almost linearly with computational load.
In addition, Pilotfish has the advantage of low latency, minimizing the time it takes to execute a transaction.Even after Pilotfish is implemented, not all transactions will be processed in this manner, as the network will automatically make decisions based on network congestion and transaction complexity.
9. Sui's On-Chain Storage
Sui's on-chain storage is very different from other common blockchains.It is one of the key advantages for Sui, although it seems to be rarely discussed.
First, let's review the storage size of a typical blockchain.
A typical blockchain is basically designed to store transaction history.As a result, there are constraints on its storage capacity, and attempts to store large amounts of data typically result in high costs.Due to these constraints, transaction-related data is usually stored on external servers (off-chain), which entails risks to data persistence.
Sui's on-chain storage, on the other hand, is fully integrated into the blockchain architecture, allowing data to be stored directly on the blockchain.The ability to store all data on-chain is critical to ensuring data security, tamper-resistance, and censorship-resistance.
By storing data directly on-chain, Sui avoids reliability and persistence risks and ensures high data availability.
Such on-chain storage in Sui is a powerful tool, especially for developers.Developers will be able to store all data related to smart contracts, NFTs, and other applications on the blockchain.
It is also possible to store data as complex objects and integrate them with other on-chain data.This eliminates the risk of partial data loss and provides users with immutable and reliable data.
In addition, Sui has a unique economic model in place, ensuring the economic sustainability of data through a "storage fund" mechanism that makes Sui's storage fund affordable for everyone to use.
This storage fund, which will be explained in more detail in the tokenomics section, consists of storage fees collected as part of the commission on every transaction, and pays validators to ensure the availability of data.
10. Various Other Sui Technologies/Protocols
Sui has a full range of functions as an infrastructure.If I were to introduce each and every feature in detail, even a long article would become even longer, so I will briefly introduce a few of them.
Incidentally, many of these features were added in late 2023-2024, and we expect that many more will be added to Sui in the future.I imagine that this kind of flexible development is difficult to achieve with ordinary integrated blockchains, and is only possible because of the structural flexibility of Sui itself and the Move language.
10-1. for users
zkLogin
zkLogin is a login function implemented on the Sui blockchain.Users can securely log in using cryptographically proven credentials without having to reveal personal information or passwords using zero-knowledge proof technology.
Specifically, users will be able to use their existing Web2 account, such as a Google account or Apple ID, to lock-in to Sui, but the user's Web2 account will not be revealed to anyone.User information is encrypted using zero-knowledge proof and proven correct without revealing that information to verifiers.This provides a reliable login process while protecting user privacy.
zkLogin reduces the risk of data breaches and account hacking and serves as a secure authentication mechanism for distributed applications (dApps) and platforms.The technology further enhances the authentication process on the blockchain, improving the user experience and enhancing security.
Stashed
A feature that once started under the name "zkSend" but has now been rebranded and is now called "Stashed", Stashed allows users to use a web-based Sui Wallet to store, send, and receive assets without the need for a traditional hosted wallet.Stashed allows users to store, send, and receive assets without the need for a traditional hosted wallet.
When sending assets, users can generate a web link that can be shared with others.The recipient simply clicks on the link to claim the shared asset and deposit it in a designated Stashed wallet.The sender can see all the links they have created and whether they have been claimed, and can generate new links to share with others as needed.
Stashed wallet creation can be combined with zkLogin to create a wallet using a regular Web2 service account (e.g. Google or Twitch).This wallet can receive assets, hold assets, send assets, and connect to Sui applications.
SuiLink
SuiLink facilitates the movement of assets and data between different blockchains, allowing users to seamlessly utilize multiple platforms.This technology has the potential to significantly improve interoperability across the entire blockchain ecosystem.
This feature enhances interoperability between different blockchains and allows for seamless movement of data and assets.SuiLink is a soulbound token (SBT) introduced on the Sui blockchain.
This soulbound token is used to prove ownership of a user's Sui address and connected Ethereum and Solana addresses.This technology allows users to link their identities across different blockchains and be rewarded for their activities on each network.
SuiLink is easy to use, maintains the security of private keys, and is broadly compatible with Ethereum and Solana wallets.SuiLink is easy to use and has extensive compatibility with Ethereum and Solana wallets while maintaining the security of private keys.It also offers the convenience of managing multiple wallets from a single interface with no link creation fees or gas charges.
SuiNS
SuiNS (Sui NameService) is a name service on the Sui blockchain.SuiNS has several innovative features compared to traditional blockchain name services: SuiNS allows users to own their name service as an NFT, enabling them to have a live digital identity independent of a central authority.
SuiNS identifiers are also set to expire and must be renewed periodically.(Names that are no longer in use are re-supplied to the market.)With these features, SuiNS sets a new standard for self-sovereign digital identity on the Sui blockchain.
10-2. For Developers
Kiosk
Kiosk is a framework for selling and displaying digital assets on the Sui blockchain, allowing developers to easily set up stores and trade NFTs and other digital assets.Built-in, it allows commerce to take place directly on the blockchain without relying on external services.
The framework provides a mechanism for creators to set royalties on their works and still earn revenue on future resales.For example, if an artist sets a 3% royalty on an NFT, 3% of the profit will be paid to the artist each time the work is resold.This creates an incentive for creators to earn ongoing profits and promotes the provision of quality content.
Kiosk is attractive because it is configurable with simple code and can be easily used by anyone from individuals to large marketplaces.Kiosk also supports secure ownership transfers and offers a wide range of features such as auctions and custom transaction policies that will shape the future of e-commerce in the Sui ecosystem.
Enoki
Enoki is a SaaS platform from Mysten Labs, a powerful tool for companies to enable the next generation of customer experience using the Sui blockchain.Enoki is designed to simplify the adoption of blockchain technology, especially for companies without expertise or large resources.Enoki is designed to simplify the adoption of blockchain technology, especially for companies that do not have the expertise or significant resources to use it quickly.
Through Enoki, businesses can seamlessly integrate Sui Wallet into their existing services and offer users true ownership of their digital assets.In addition, by leveraging Sui features such as zkLogin and sponsored transactions, users can easily participate in the Web3 experience and no longer have to pay for gas.
Enoki leverages the transparency of the Sui blockchain to help companies track transactions and customer activity in real time to support data-driven decision making.Through this platform, companies can directly evaluate the effectiveness of their marketing strategies and optimize customer engagement.
Through its APIs and SDKs, Enoki also provides solutions for companies to easily incorporate blockchain technology to streamline their operations and enhance the customer experience.Enoki offers companies new engagement strategies using blockchain technology as a means to enhance their customer relationships andIt is being utilized by.
Walrus
Walrus serves as the data storage and data access layer of the Sui blockchain and is intended to store large amounts of data in a distributed manner while keeping it quickly and reliably accessible.The system utilizes error correcting codes and data partitioning techniques to ensure high redundancy and data sustainability.
Walrus operates on server-based cloud storage, which is different from Sui's on-chain storage, and is designed to efficiently store and keep large amounts of data accessible.
Walrus utilizes error correcting codes and data partitioning and reconfiguration techniques to ensure distributed data storage and redundancy.In other words, it provides fast and reliable data access while preventing accidents such as data loss or tampering.
Walrus also provides an economic incentive to maintain data availability, providing a sustainable storage solution while reducing the cost of data storage.It is envisioned to be available at a cost that can be considered and will be an attractive third-party tool for external developers.
Use cases envisioned for this technology include NFT and other repositories, AI-related data storage, and Layer 2 soluble support.This was just announced in June 2024 and is not yet implemented at this time.
DeepBook
DeepBook is the first native liquidity layer protocol on the Sui blockchain.It leverages the Central Limited Order Book (CLOB) to provide liquidity to the DeFi protocol and gaming applications on Sui.
First, let's discuss the Central Limited Order Book (CLOB), a traditional trading system that matches sell and buy orders in real time.Sellers can sell an asset at a limit order or market price, and buyers can buy an asset at the market price or at a specific price; CLOB's automated matching feature ensures efficient price discovery and fair trading.
This means that DeepBook does not rely on the liquidity balance in the pool as AMMs (automated market makers) do, which reduces slippage even on large trades.In an order book based trading system, all orders are transparently recorded and publicly disclosed.This provides an environment that is difficult for unauthorized price manipulation and opaque trading.
Developers can easily incorporate trading functionality into existing applications using the SDK provided by DeepBook.New projects can also easily enter the market by utilizing DeepBook's liquidity layer.
Sponsored Transactions
Sponsored transactions are a mechanism for a third party to pay for gas for transactions executed on the Sui blockchain on your behalf.This feature is designed to allow users to execute transactions even when they do not have sufficient funds in their wallets.
For example, dApp developers and companies can shoulder transaction fees to improve the user experience.This would allow new users or users with limited funds to use blockchain services without having to worry about gas prices.
Sponsored transactions promote the widespread use of blockchain technology and provide an easy environment for participation, especially for new users.
This mechanism also allows application providers to promote the use of their services by charging transaction fees as part of their user acquisition strategy.
This is the "Sui Complete Review (Part 2)".Finally, tomorrow will be the final update of the three-part series.It may be difficult to read it all in one sitting as it is quite voluminous, but we encourage you to watch it over and over again!
Disclaimer:I carefully examine and write the information that I research, but since it is personally operated and there are many parts with English sources, there may be some paraphrasing or incorrect information. Please understand. Also, there may be introductions of Dapps, NFTs, and tokens in the articles, but there is absolutely no solicitation purpose. Please purchase and use them at your own risk.
About us
🇯🇵🇺🇸🇰🇷🇨🇳🇪🇸 The English version of the web3 newsletter, which is available in 5 languages. Based on the concept of ``Learn more about web3 in 5 minutes a day,'' we deliver research articles five times a week, including explanations of popular web3 trends, project explanations, and introductions to the latest news.
Author
mitsui
A web3 researcher. Operating the newsletter "web3 Research" delivered in five languages around the world.
Contact
The author is a web3 researcher based in Japan. If you have a project that is interested in expanding to Japan, please contact the following:
Telegram:@mitsui0x
*Please note that this newsletter translates articles that are originally in Japanese. There may be translation mistakes such as mistranslations or paraphrasing, so please understand in advance.