【Flatcoin explanation②】 What is the decentralized flatcoin "SPOT"? / @SPOTprotocol
The keywords are "tranche" and "rotation".
Good morning.
Mitsui from web3 researcher.
Today, as Flatcoin Commentary #2, we will discuss the decentralized flatcoin "SPOT".
📕Review
🪙What is a SPOT?
💬Blockchain for Theory
📕Review
First, let's review a few things.In the first part of this article, I explained the concept of flat coins and the specific project, AMPL.
To be honest, it is difficult to understand the detailed concept and technology, so we have made this article so that you can only understand the overview at a glance, so if you have not seen it yet, please read this first.
This article is based on the AMPL, and explains the "SPOT" flat coin based on the AMPL.
There is also a very detailed explanation of the "SPOT," but it gets complicated when you get into the details, so this article will present the big picture.For more details, please refer to the documentation.
Then let's go.
🪙What is a SPOT?
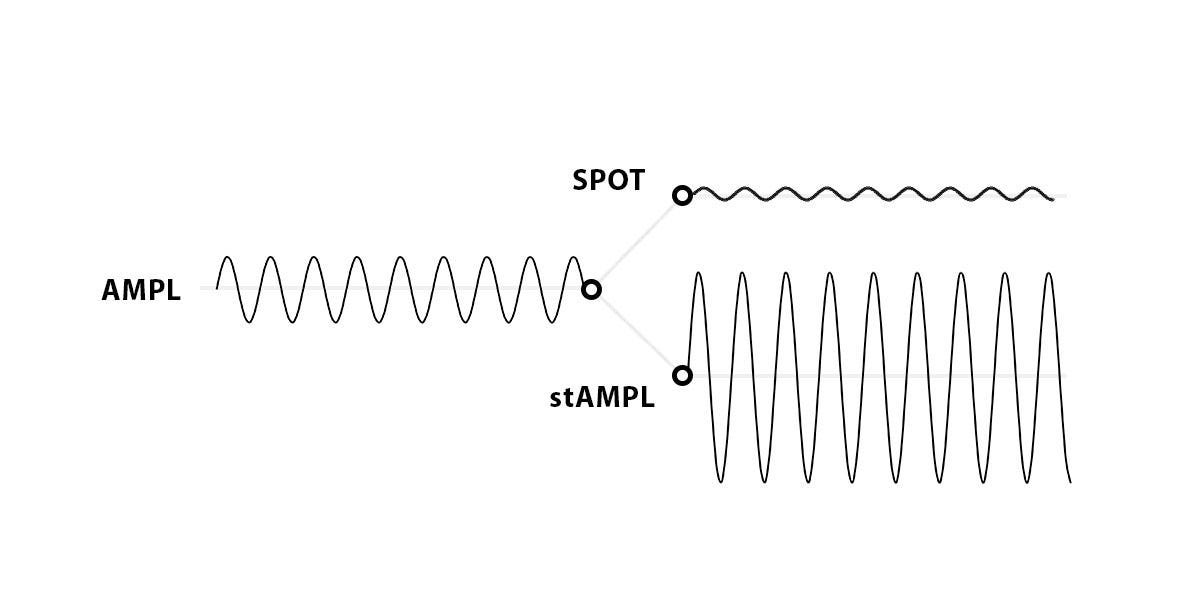
The "SPOT" is a decentralized flatcoin, issued from the AMPL.
AMPL is a crypto asset that tracks 2019 CPI-adjusted dollars, and is characterized by a fluctuating supply.However, it abandons short-term price stability and is designed to always stabilize to its original price over the medium to long term.
In other words, AMPL is a token whose price is stable in long units but volatile in short moments.The high volatility of a token that is used on a daily basis cannot fulfill the role of a flat coin.
Flatcoin is only intended to serve as a currency and to be used in everyday life, so it must have low volatility.Therefore, the SPOT token was created based on the AMPL; the SPOT is the flatcoin.
So why is there no volatility in SPOT based on AMPL, which is volatile in the short term?
The key words are tranche and Rotation".
The SPOT protocol works by splitting a medium volatility asset (AMPL) into a high volatility derivative (stAMPL) and a low volatility derivative (SPOT).
This division is called a tranche, and we will first explain tranches.
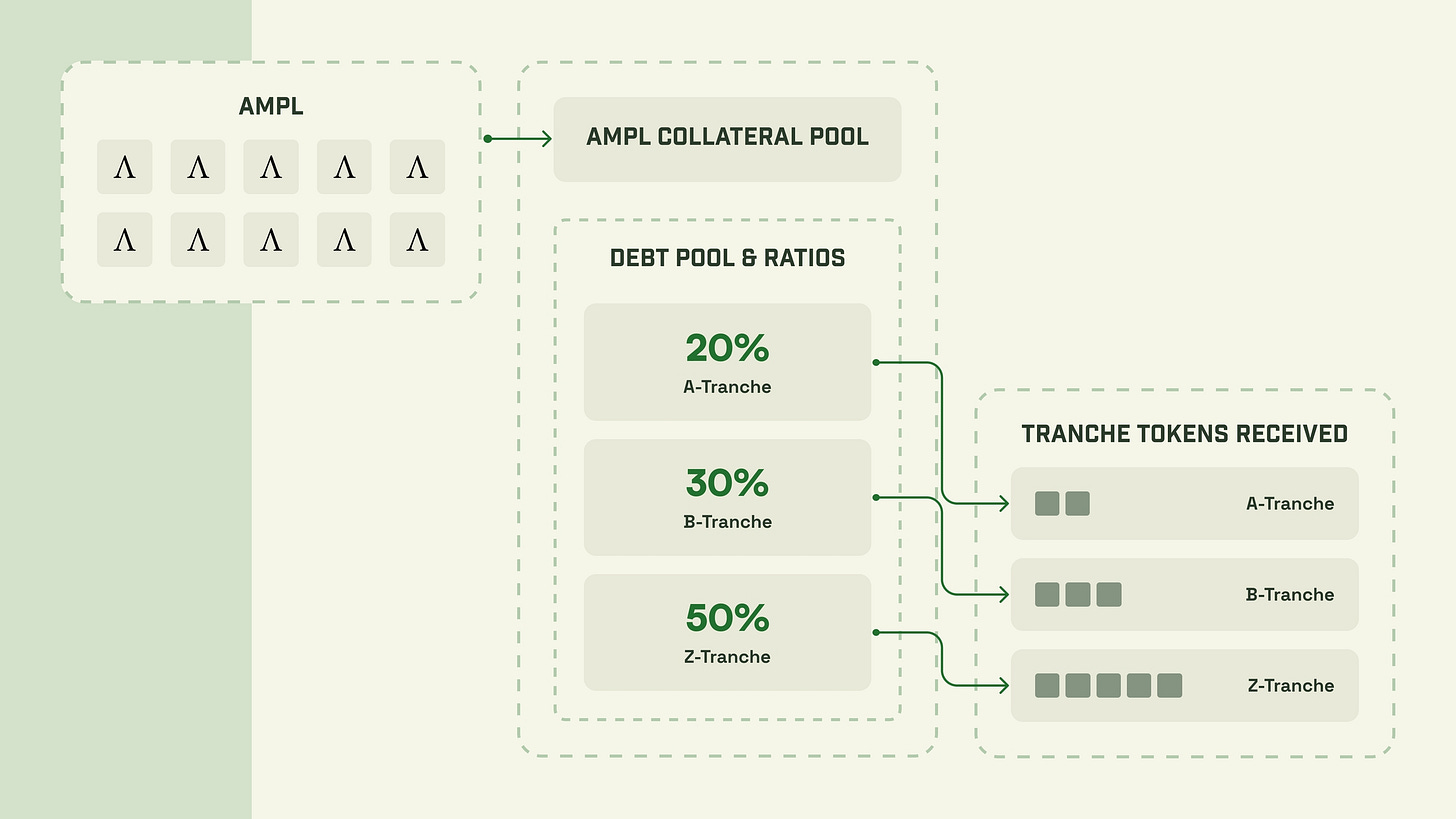
A tranche is a term used in finance and investment to describe a large bond or securitized product that has been divided into multiple parts based on characteristics such as risk and maturity date.Simply put, it is one investment instrument divided into parts according to its risk.
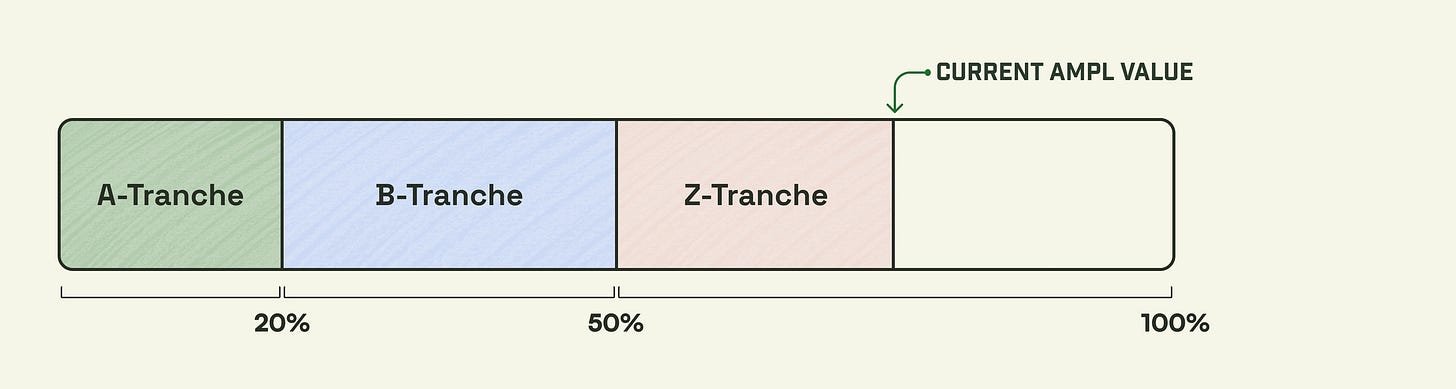
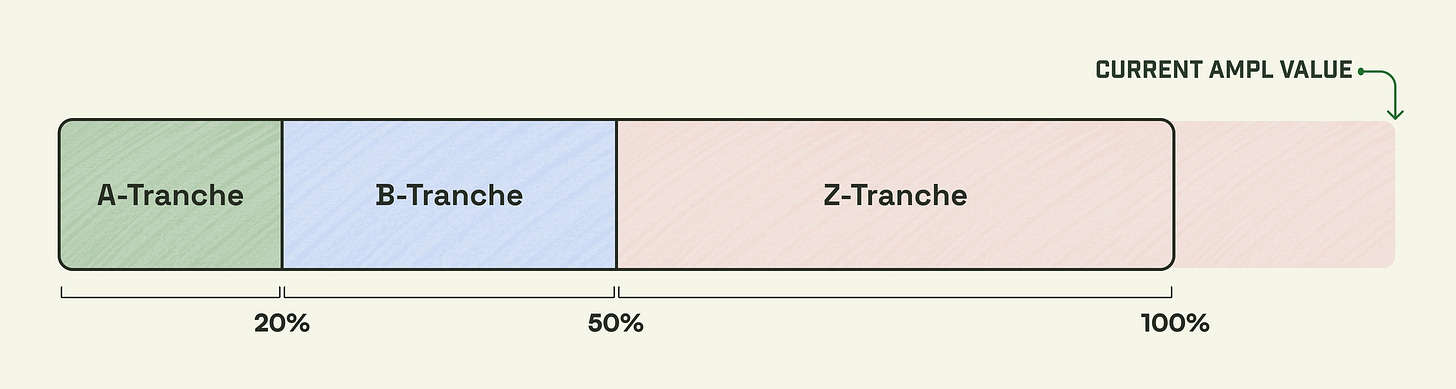
For example, the following is an example of an AMPL divided into tranches, with risk and maturity dates separated by A, B, and Z, respectively, receiving 20%, 30%, and 50% tranches.
A tranche is the safest 20% of AMPL's value
B tranche is the median 30% of AMPL's value
Z tranche is the top 50% of AMPL's value
respectively.
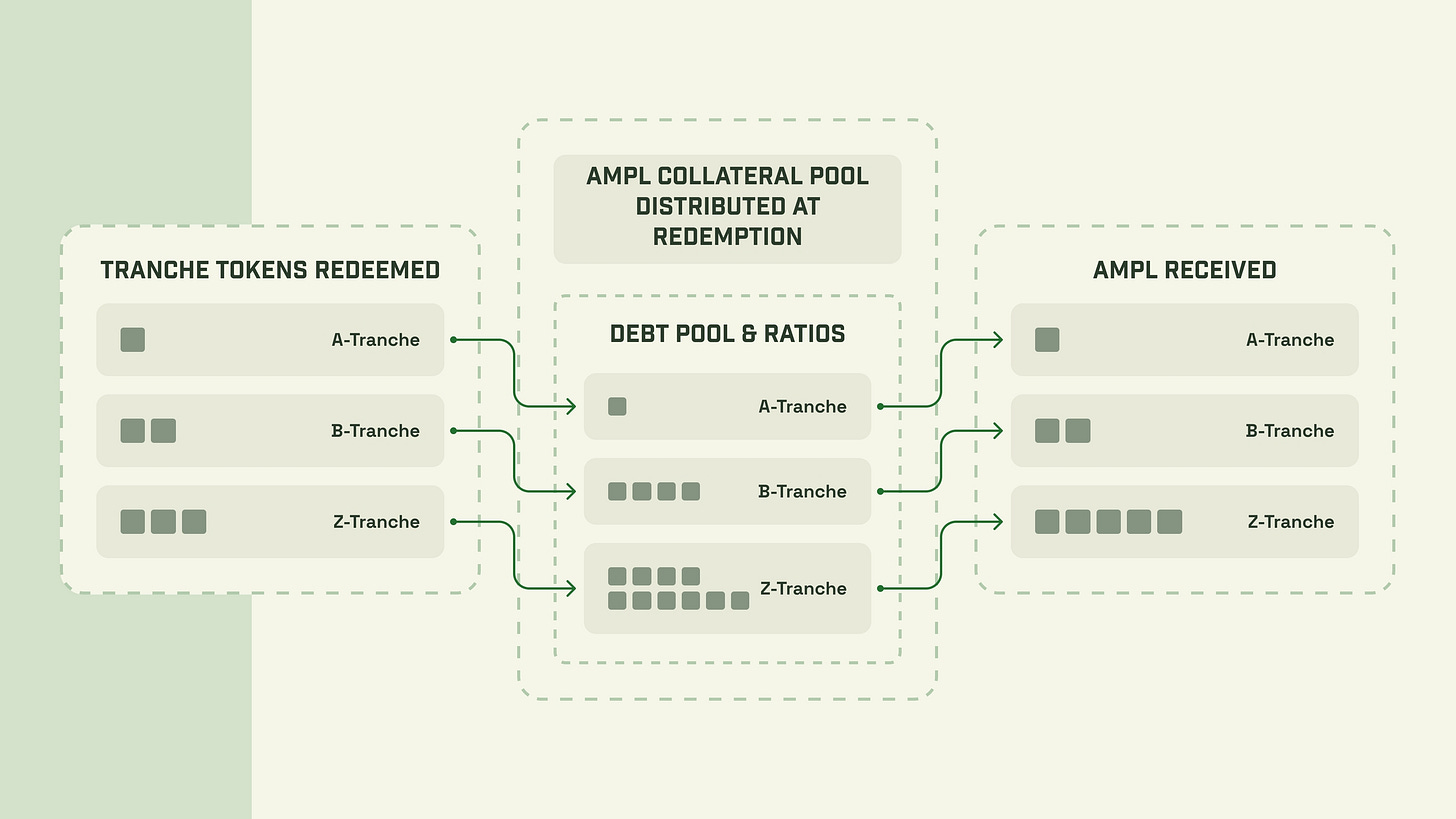
The actual differences in risk profiles between different tranches arise from the behavior of the bonds at maturity.When the bonds mature, the collateral is returned to the tranche owners in a waterfall fashion.The top tranche (A tranche) is repaid in full first on a 1:1 basis, then the bottom tranche (Z tranche) is repaid last, but all remaining funds are paid to the Z tranche.
In the following cases where the value of a tranche has decreased prior to redemption
A tranche will be repaid in full 1 AMPL for each A tranche.
The B tranche will be repaid in full, 1 AMPL per B tranche.
The Z tranche will be paid the remainder, about 0.5 AMPL per Z tranche
Conversely, in the following cases where the value of a tranche has increased,
A tranche will be repaid in full 1 AMPL for each A tranche.
The B tranche will be repaid in full, 1 AMPL per B tranche.
The Z tranche will be paid the remainder, approximately 1.2 AMPL per Z tranche.
After this process, the holder of the A or B tranche will be fully restored, but will not receive any benefit from the increased AMPL value; the Z tranche holder will receive all benefits in exchange for the additional risk.
The value increase of a tranche in AMPL is worth, for example, the token price.If the price increases within a certain period of time, the return is returned to the holder of the high-volatility tranche.
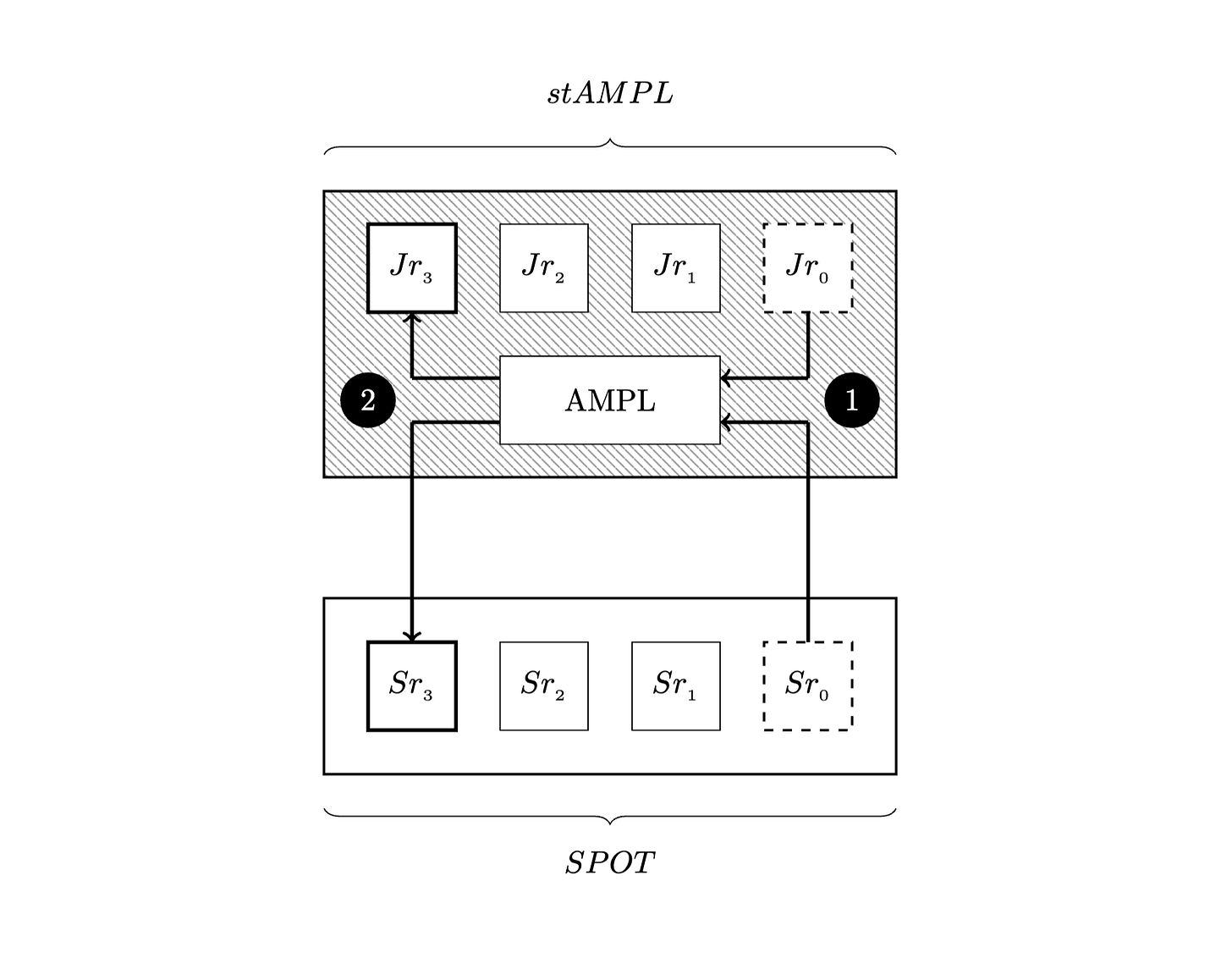
The SPOT protocol utilizes exactly this tranche.It works by splitting a medium volatility asset (AMPL), which fluctuates in the short term, into a high volatility derivative (stAMPL) and a low volatility derivative (SPOT).
The A and B tranches in the above are the SPOT and the Z tranche is the stAMPL.
However, of course, tranches have a redemption period.After a certain period of time, they are redeemed and return a return on the price change at that point in time.However, if a SPOT is redeemed after a certain period of time, it will not function as a currency.
This is where the other key word "rotation" comes in.This mechanism keeps exchanging maturing tranches with newly issued tranches in the collateral set of the SPOT automatically; the tranche matures in 28 days, but the tranches are constantly rotated through this mechanism, and the SPOT continues to exist.
It's a little difficult, isn't it?
You can find more details in the Documentation.How the tranches will be implemented, the rotation procedure, the rationale for keeping prices stable with this structure and how to target it if it happens.
However, writing about this would get crazy complicated, so in this article I want to tell you that the root idea is that a flat coin SPOT is achieved by tranching and rotating the SPOT.
By tranching tokens (indices) based on CPI-adjusted dollars like AMPL into high volatility stAMPL and low volatility SPOT, and then continuing to rotate them, a flat coin will be realized.
Incidentally, it seems to be a recently proven financial theory that when tranched into high and low volatility, low volatility assets stabilize in price.
💬Blockchain for Theory
Now, over the course of two articles, I have explained flatcoin using the specific protocols AMPL and SPOT protocols as examples.It may have been a complicated explanation as it required quite a bit of financial knowledge.
I myself am not that knowledgeable about finance, so it took me a while to understand.And I thought it would be quite complicated if I explained everything, so I only explained the big picture and left out the details.
First of all, I thought the mechanism and concept of flatcoin was very interesting, but I realized once again that blockchain is only a technology, and what is important is the concept and knowledge that underlies it.
Finance is definitely one of the most important things that blockchain can innovate, but without financial knowledge to begin with, you may not be able to understand the innovativeness of the new protocol or even create a product in the web3 domain.
Successful entrepreneurs in the web2 space also have years of experience working in that space and are familiar with it, and they use the Internet to streamline some of it to create projects that users will use.Naturally, the Internet is a tool, and the premise is industry understanding.
Many people in the web3 industry, including myself, start with the idea that "blockchain is interesting," so we tend to think about what we can do from the blockchain's point of view.However, of course, in order to create something that people can use, you need to think based on real-world issues.
For example, someone who worked in the financial industry would need to use blockchain to create something, or someone in the gaming industry would need to use blockchain to solve that negative based on industry knowledge and raw challenges.
As I learned more about the financial industry through researching Flatcoin, I was reminded of the obvious.Personally, I don't think it's wrong to think in terms of blockchain starting point since it's a new innovation, but it's not good to think only in that perspective.
We will again explore the possibilities of blockchain while also learning about the peripheral areas.
This is a description of flat coins!
🔗Reference/image credit: HP / DOC / X
Disclaimer:I carefully examine and write the information that I research, but since it is personally operated and there are many parts with English sources, there may be some paraphrasing or incorrect information. Please understand. Also, there may be introductions of Dapps, NFTs, and tokens in the articles, but there is absolutely no solicitation purpose. Please purchase and use them at your own risk.
About us
🇯🇵🇺🇸🇰🇷🇨🇳🇪🇸 The English version of the web3 newsletter, which is available in 5 languages. Based on the concept of ``Learn more about web3 in 5 minutes a day,'' we deliver research articles five times a week, including explanations of popular web3 trends, project explanations, and introductions to the latest news.
Author
mitsui
A web3 researcher. Operating the newsletter "web3 Research" delivered in five languages around the world.
Contact
The author is a web3 researcher based in Japan. If you have a project that is interested in expanding to Japan, please contact the following:
Telegram:@mitsui0x
*Please note that this newsletter translates articles that are originally in Japanese. There may be translation mistakes such as mistranslations or paraphrasing, so please understand in advance.