【ERC-8004】Standard Specification for Trustless Agents / Provides Identity, Reputation, and Validation to compensate for the "trust deficit" in existing protocols like A2A and MCP
The importance of blockchain as a foundation for trust and transactions is increasing.
Good morning.
I’m Mitsui, a web3 researcher.
Today I researched ERC-8004. Rather than delving into complete technical details, I will explain its significance, overview, evolution, and future prospects.
What is ERC-8004?
Technical Specifications
Use case
Transition and Outlook
The importance of blockchain as a foundation for trust and transactions is increasing.
TL;DR
ERC-8004 is a standard that provides a minimal trust layer (Identity/Reputation/Validation) on Ethereum, enabling AI agents to collaborate without prior trust relationships. It complements the “trust deficit” in existing protocols such as A2A and MCP.
Identity uniquely registers agents as ERC-721 (NFT) tokens. Reputation records feedback (scores, tags, evidence URIs/hashes) based on signed approvals. Validation standardizes third-party verification requests and results, connecting diverse verification models (stake replay, zkML, TEE, human adjudication, etc.).
These verification methods can be declared within Identity’s supportedTrust, positioning blockchain as a neutral trust and transaction foundation for automated transactions combined with x402 settlement, and for the future agent economy (mainnet deployment, Devconnect announcement, dAI team advancement).
What is ERC-8004?
ERC-8004 is a new standard (ERC specification) proposed on Ethereum, aiming to establish a minimal trust layer for autonomous services—referred to as “trustless agents”—such as AI agents and bots.
The background to the creation of this standard included a lack of trust between AI agents, the difficulty of visualizing evaluations, and the limitations of existing protocols.
Below, each will be explained.
◼️The “Trust” Problem Among AI Agents and the Challenge of Visualizing Evaluation
When AI agents interact with each other, the question arises: “Is this counterpart truly trustworthy?” Currently, there is no common mechanism to objectively demonstrate an agent’s past performance.
For example, even if you find an AI agent online that performs data analysis, there is no unified “rating score” to verify its reputation or past performance. As a result, users have no choice but to judge its reliability by trial and error—gathering word-of-mouth feedback and documentation or actually testing it themselves.
As a result, the following phenomena may occur.
The rampant activities of unscrupulous agents
Malicious developers could create new agents with no reputation one after another, take on requests to extract value, and then disappear. Without reliable identity verification, preventing such impersonation and fraud becomes difficult.Loss of an excellent agent
Conversely, even sincere and capable agents cannot carry over their track record (portable reputation) and must build trust from scratch every time they enter a new market. Since their evaluations get reset everywhere, they tend to be treated as “newcomers” each time, despite their true excellence.
In this current state where “visualization of trust” is lacking, it poses a major obstacle to building an “agent economy” where AI agents engage in full-scale transactions and collaboration. It’s akin to trading with strangers in auctions or flea markets without any evaluation system, making it difficult to entrust them with confidence.
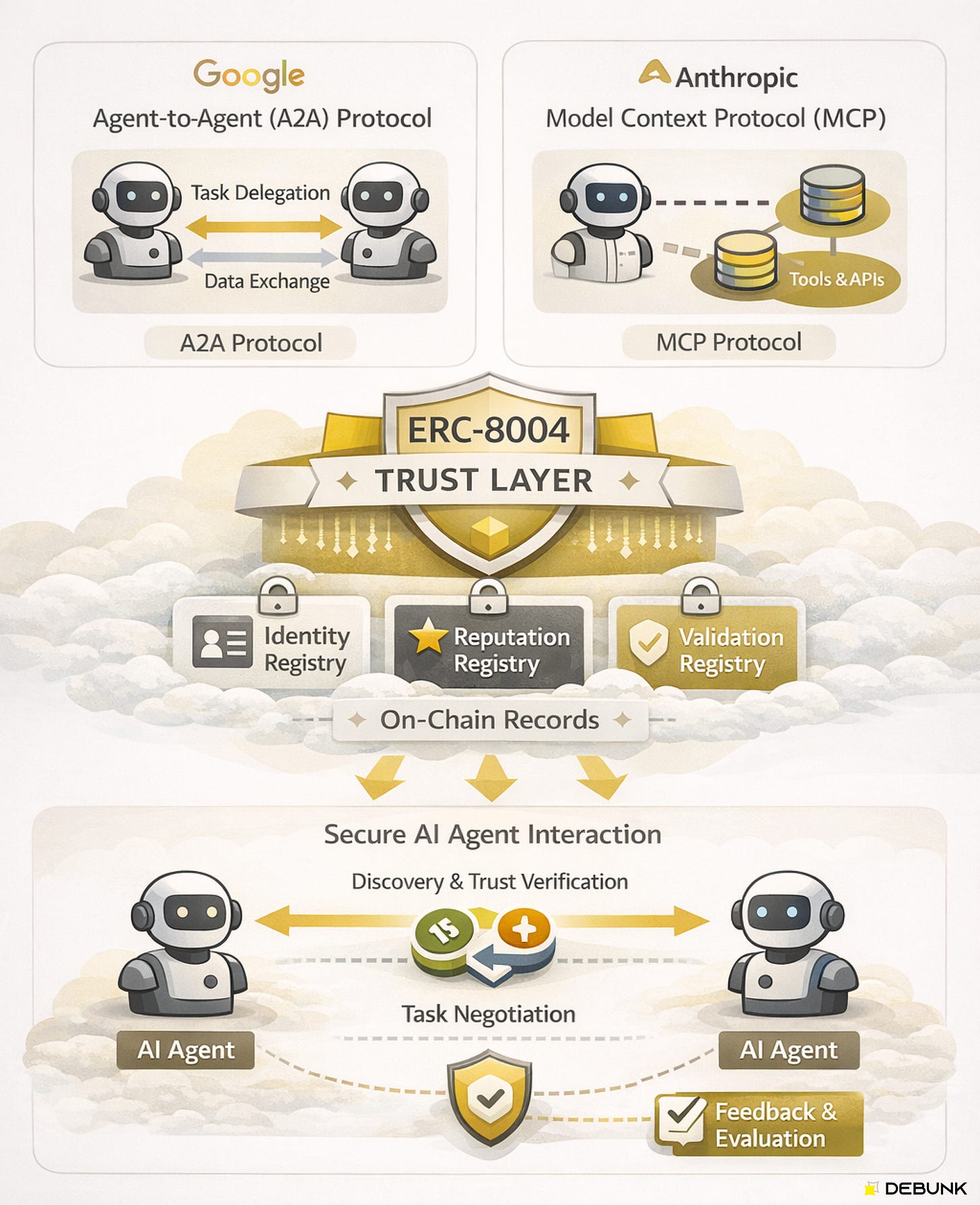
◼️Limitations of Existing Protocols (A2A, MCP, etc.) and the Role of ERC-8004
Currently, several protocols have been proposed and are being utilized to support interactions between AI agents.
Notable examples include Google’s Agent-to-Agent (A2A) protocol and Anthropic’s Model Context Protocol (MCP). A2A is a communication standard enabling agents to delegate tasks to each other or discover one another, while MCP is a standard for AI systems like LLMs to access necessary external data and tools.
However, these existing protocols do not incorporate mechanisms to establish trust. For example, A2A is designed assuming collaboration between trusted parties, such as within an enterprise, and does not account for building trust with unknown external agents. MCP is also intended for agents to access data and lacks functionality to assess the trustworthiness of other agents.
ERC-8004 serves to address this shortcoming.
ERC-8004 is an extension standard that adds a “trust layer” on top of existing A2A, enabling agents to discover and select each other, and conduct secure transactions even without prior trust relationships.
Details will be discussed later, but ERC-8004 introduces three on-chain registries to manage agent identity information, reputation and track record, and validation records on the blockchain.
If A2A and MCP define how agents communicate and share data, ERC-8004 provides the information foundation for determining whether that counterpart is trustworthy.
In fact, it is said that only by combining ERC-8004 with these protocols can the full stack of agent-to-agent transactions (communication + settlement + trust evaluation) be completed.
For example, the following workflow is envisioned: “Verify the counterparty’s identity and reputation using ERC-8004 (who they are and their track record), conduct specific negotiations via A2A/MCP, settle using a separate standard called x402, and leave evaluation feedback on ERC-8004 once the work is completed.”
Furthermore, by building these crucial standards for the AI agent economy on the neutral infrastructure of Ethereum, we ensure they are equally accessible to all AI agents.
Technical Specifications
Next, I’ll explain the technical specifications. Since providing complete details is difficult, I’ll limit myself to an overview here. If you’d like to delve deeper, please refer to the documentation.
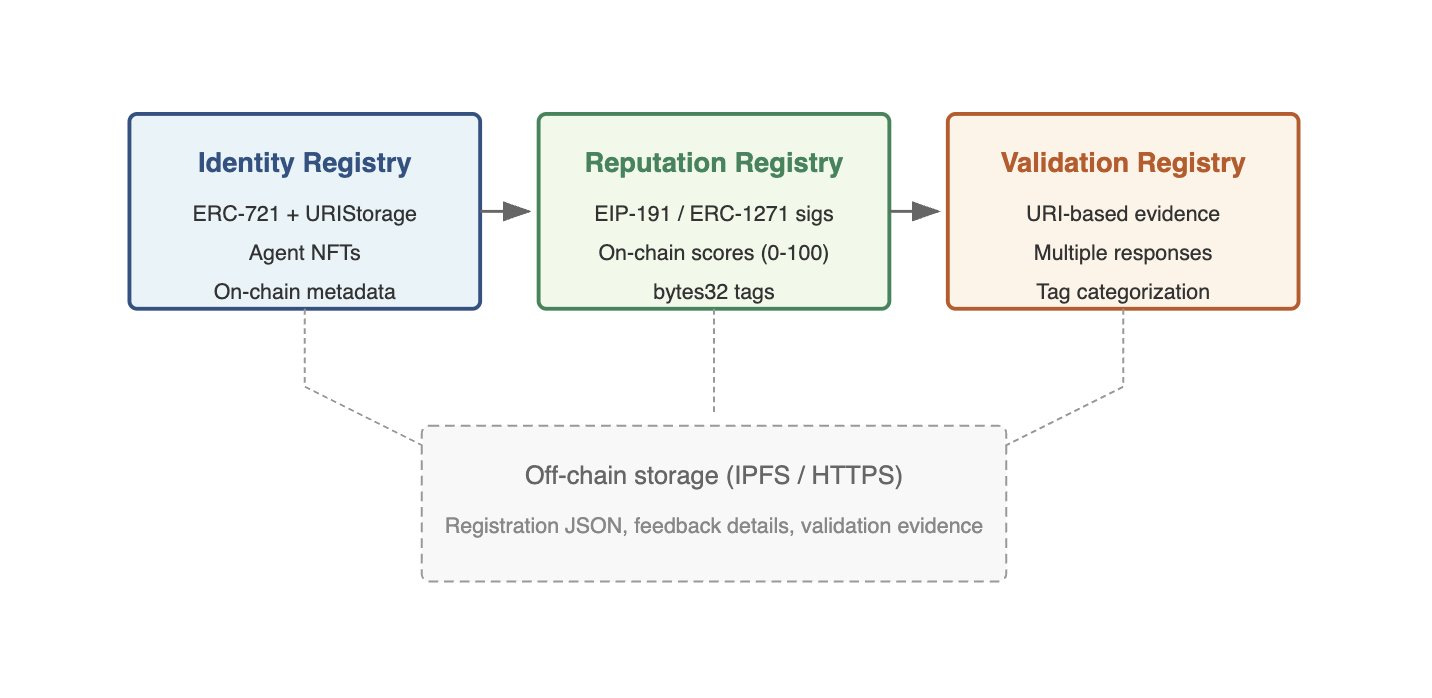
ERC-8004 provides three lightweight on-chain registries (Identity, Reputation, Validation), adopting an approach that leaves all other application-specific logic off-chain. It builds a flexible trust model while keeping only the minimum necessary data on-chain.
◼️Identity Registry
Identity Registry is a mechanism that assigns a globally unique on-chain ID to each agent. Technically, it utilizes the URI storage extension of the ERC-721 standard (NFT) to register and manage agents as NFTs.
This enables each agent to obtain a highly censorship-resistant and portable identifier, allowing them to be viewed and transferred from existing NFT-compatible wallets and marketplaces.
Each agent is uniquely identified by the following four elements.
namespace:Chain Family Identifier (EVM-based chains)eip155(using)chainId:Blockchain Network IDidentityRegistry:Identity Registry Contract AddressagentId:Token ID issued in the registry (ERC-721)tokenId(synonymous with)
The owner of an ERC-721 token is the owner of its agent, and due to the nature of the NFT, it is possible to transfer ownership or delegate management permissions (such as updating URIs).
Additionally, each agent NFT’stokenURIIt stores a link to an off-chain “agent registration file.” This registration file (e.g., JSON on IPFS) contains the agent’s public profile information, such as:
Basic Information:
type(schema identifier),name(Agent Name),description(Explanation),image(Image)Connection Endpoint:List of URIs by communication protocol and identification method supported by the agent (e.g., for A2A)
.well-known/agent-card.jsonMCP endpoint, ENS name, DID, agent wallet address, etc.Registration History:
registrationsA list of agent IDs and registry information (which can be multiple, such as registrations on other chains)Response Reliability Model:
supportedTrustThe types of trust guarantees supported by agents (such as reputation/economic collateral/TEE, etc., as described later)
This structure enables agents to publish their capabilities and contact points in a machine-readable format.
For example,endpointsand includes multiple communication methods (A2A, MCP, ENS name, DID, wallet address, etc.),supportedTrustYou can declare which types of trust mechanisms it supports.
Please note,supportedTrust If the field is empty or unset, the agent will be treated as participating only for discovery purposes and not for trust scoring.
The Identity Registry contract itself extends ERC-721 and optionally includes a function to store on-chain metadata (setMetadata/getMetadataIt also features smart contracts and events. This enables the storage of simple information (such as agent names or wallet addresses) directly on-chain for direct reference by smart contracts.
◼️Reputation Registry
Reputation Registry is an interface that standardizes the recording and publication of agent feedback (reputation information). Clients (agent users or other agents) can post feedback after interacting with an agent, leaving content such as scores, tags, and off-chain report URIs as evidence.
The basic feedback information has the following structure.
Score:Quantitative evaluation (e.g., 0 to 100 points)
Tag:Any label (a short identifier indicating a category or context)
Evidence URI:Link to the off-chain report containing detailed logs, deliverables, payment receipts, and other relevant documentation
Hash:KECCAK-256 hash of the above off-chain report (for tamper-proofing)
By designing the system to record only lightweight evaluation signals on-chain while storing detailed data off-chain, we achieve a balance between reliability and cost.
On-chain, event issuance enables tracking and aggregation of transaction histories, while advanced evaluation algorithms and analysis are handled by off-chain services.
To prevent spam-like false evaluations, ERC-8004 requiresPre-approval from the agentWe have implemented a mechanism. Specifically, the agent (server-side) issues a signed token to the client that serves as “proof of feedback posting authority.” Only clients possessing this token can write evaluations on-chain.
This token contains information such as who can evaluate, until when, and up to how many times (e.g., target agentId, client address, maximum number of posts, expiration date, etc.), and is ERC-8004 compliant.giveFeedbackIt is validated when the function is called.
Additionally, a feedback retraction feature is available, allowing posters to invalidate erroneous or unwanted ratings after submission.
◼️Validation Registry
The Validation Registry is a framework for requesting third-party verification of an agent’s deliverables and actions and recording the results.
An independent validator checks whether the agent’s output is correct or meets expectations, and by recording the result (pass/fail or score) and evidence on-chain, it ensures higher reliability.
The Validation Registry is designed as a generic interface independent of verification methodologies, enabling flexible integration of various verification models.
The verification process consists of two main stages.
Verification Request
The agent owner or operator records a request in the Validation Registry for their work to be validated. Specifically, they register which validator should validate which agent’s deliverables using which data.Verification Response
The designated validator performs verification work off-chain and posts the results to the Validation Registry.
The Validation Registry itself serves a simple role focused solely on storing results and event notifications; it does not include incentive design or staking/slash logic.
Therefore, independent economic networks (protocols handling validators’ stakes, rewards, and penalties) can be freely built on top of this standard. Similarly, the standard does not dictate which validation methods should be adopted. For example, it is envisioned that diverse validation models such as the following could coexist:
Stake-backed replay:Other participants (validators) re-execute the agent’s tasks and verify the results; in cases of fraud, the deposited collateral (stake) is confiscated to ensure integrity.
Zero-Knowledge Machine Learning Verification (zkML):Demonstrate the validity of machine learning model inference results using zero-knowledge proofs.
TEE Oracle Verification:Execute code within a trusted execution environment (such as Intel SGX) and demonstrate its legitimate execution alongside a hardware-originating proof.
Human judge’s decision:A model where results are confirmed and adjudicated through human judgment, such as governance voting.
In this way, the Validation Registry standardizes the interface for “requesting and recording verification results,” thereby providing a foundation for specialized services for each verification method—such as replay networks, zkML probers, TEE providers, and distributed arbitrator networks—to interoperate.
Having multiple verification models enables a layered defense approach: simple reputation-based trust suffices for low-risk tasks, while high-value, high-risk tasks can be secured by adding economic or cryptographic verification.
And this verification method is written into the supportedTrust field within the aforementioned “Identity Registry.” By doing so, the AI agent can automatically select the agent to negotiate with, taking into account the verification method based on the task at hand.
◼️Summary
ERC-8004 is a standard that provides a minimal and neutral “trust layer” on Ethereum, enabling AI agents to collaborate without prior trust relationships.
Through three lightweight on-chain registries—Identity, Reputation, and Validation—we record only the essential facts needed for trust assessments, such as an agent’s identity, past reputation, and verification results, in a common format. The specific evaluation logic, verification methods, and economic design are delegated off-chain.
In particular, the verification methods that the agent can handle
supportedTrustBy declaring in advance and recording actual verification results through the Validation Registry, agents can automatically determine whether “reputation alone is sufficient” or “economic collateral and cryptographic verification are required” based on a task’s importance.This enables ERC-8004 to realize the foundation of an open agent economy with scalability and interoperability, not locked into a single trust model.
Use Case
The “Open Agent Economy” envisioned by ERC-8004 promotes collaboration among autonomous agents across various fields of web3 and AI.
The following examples are among the primary use cases currently under consideration:
AI Agent Marketplace
In the open market for general-purpose or specialized AI services (e.g., document generation AI, code audit AI), clients can search for and compare agents using trust scores based on ERC-8004. Clients can select AI assistants with high reputation scores based on past task completion records and customer satisfaction. For high-value tasks, additional safeguards like zkML verification can be applied, enabling tailored usage.DAO Governance Support Bot
The governance assistant agent, which analyzes proposal content and provides voting recommendations within the DAO, utilizes the ERC-8004 reputation and verification layer. It accumulates reputation scores based on the accuracy of proposal analysis and past performance. For critical proposals, it includes verification results from Trusted Oracles or human audits, providing community participants with grounds to trust the bot’s advice.Cross-organizational task matching
In cross-organizational task marketplaces where Company A’s AI agent commissions tasks from another agent at Company B, the reliability of trading partners is visualized using ERC-8004. This enables secure use of external AI services based on public reputation, past payment history, and validation records—even in scenarios where collaboration was previously difficult without direct trust between organizations. It forms the infrastructure for a new B2B collaboration model where “AI agents exchange work across corporate boundaries.”Insurance for Agents / Slash
Utilization in insurance markets to prepare for service failures or fraudulent activities by autonomous agents. For instance, premiums could be calculated based on historical reputation scores and verification histories, or guarantee plans tailored to service quality could be offered. Additionally, while a separate protocol, a guarantee fund combining validator stake slashing (collateral confiscation) could be established. This would enable risk management solutions such as automatic payouts based on ERC-8004 validation results (success/failure).On-chain game NPC agent
Applying ERC-8004 to autonomous NPCs and trader bots operating within blockchain games is also being discussed as a way to enhance the fairness of the in-game economy and the reliability of the user experience. For example, publishing the transaction success rate and integrity of AI agents handling trades on the in-game marketplace as a reputation score, or having third parties verify logs for fraudulent activity, would allow players to trade with these agents with confidence.NFT and Social Graph Domain
ERC-8004-like trust frameworks can also be applied to NFT art authentication agents and content curators on decentralized social networks. For example, by recording an AI authentication agent’s appraisal history and community evaluations on-chain—such as its NFT authenticity and rarity assessments—new collectors can reliably find trustworthy experts. Furthermore, for bots performing post moderation and recommendations on decentralized social networks, recording their past history of sound operation and verification of error corrections would allow users to gather information with greater peace of mind.
As described above, ERC-8004 contributes to ensuring reliability and fostering development across various scenarios where AI and blockchain intersect. Particularly as autonomous agents utilizing LLM and similar technologies proliferate, the importance of on-chain verification of their origin, track record, and verifiability is increasing. ERC-8004 is positioned as the foundational infrastructure for this purpose.
Additionally, micropayments integrated with x402 are compatible with all of these, and autonomous asset management AI agents like DeFAI also fall under this category.
Transition and Outlook
ERC-8004 had its EIP draft published on August 13, 2025, sparking active discussions on forums like Ethereum Magicians. Subsequently, it was first deployed on various testnets. As of September 2025, the contract has been deployed on multiple testnets, including Ethereum Sepolia, Base Sepolia, Linea Goerli, and even the EVM-compatible Hedera Testnet.
Furthermore, the Ethereum Foundation (EF) recognized the importance of ERC-8004 early on and established a new AI research team, “dAI,” in September 2025. This team is led by Davide Crapis, one of the ERC-8004 proposers, and is advancing the development and adoption of ERC-8004 alongside co-proposers Marco De Rossi (formerly of Consensys) and Jordan Ellis (Google).
EF’s dAI team aims to “build a decentralized AI stack and form an AI agent economy,” planning to support the development of blockchain-AI fusion use cases starting with ERC-8004. In fact, in combination with ERC-8004, we are also working on standardizing an HTTP 402-compliant payment protocol (x402), advancing the creation of a comprehensive foundation enabling AI agents to autonomously make payments and collaborate on Ethereum.
Following approximately two months of peer review and testing, version 1.0 was completed in mid-October 2025. Proposers including Marco De Rossi (MetaMask) and Davide Crapis (Ethereum Foundation) stated, “We incorporated feedback from hundreds of researchers and industry leaders within six weeks of the August draft, resulting in significant improvements.”
These results were published online, and simultaneously, a one-day special event on ERC-8004 titled “Trustless Agents Day” was held at the Ethereum community conference “Devconnect” in Istanbul in November 2025.
The proposing team presented the vision and latest status of ERC-8004 at this event, featuring demonstrations and panel discussions. Concrete outcomes included insights gained from testnet operations (constraints in v0.4 and improvements in v1.0) and deployment plans for major L2s.
The full-scale deployment to the mainnet is rumored to be scheduled for January 16, 2026, and is expected to roll out soon.
The importance of blockchain as a foundation for trust and transactions is increasing.
Finally, we conclude with a summary and analysis.
Interest is growing not only in the crypto space but also in the AI agent economy. While we don’t yet see widespread instances of AI agents collaborating to complete tasks and make payments, it’s certain that such a world will emerge in the medium to long term.
In this context, several critical issues arise—recording evaluations, negotiations, and contracts between AI agents; handling payments; managing ownership rights—and I believe blockchain will form the foundation for all of them.
These issues are just as important as improving pure LLM performance or data and tool integration through MCPs. Without a foundation of trust and transactions, it is impossible to connect AI systems to complete business workflows.
Technically, mega-platforms could emerge. For instance, Google could develop features similar to ERC-8004 or x402. However, this would likely be built on top of Google’s centralized cloud infrastructure and become a standard usable within Gemini. As a for-profit company, it’s natural for Google to prioritize its own advantages.
That is precisely why it is meaningful to build a trust foundation between AI agents on top of blockchain—a neutral, open, and verifiable infrastructure. This will realize a world where competition arises from the applications and user experience factories built upon it, rather than from lock-in through infrastructure enclosure.
Personally, I believe the timeline is such that 2026 will still be a year of testing technologies and use cases, with the economy among AI agents truly taking off around 2027. While AI agents were much talked about in 2025, nothing truly usable emerged. It’s such a challenging field that I expect further advancements on the AI side, coupled with the maturation of blockchain’s trust and transaction infrastructure as the final piece of the puzzle.
The core ERC-8004 will continue to track information even after the mainnet launch!
That concludes our research on “ERC-8004”!
Reference Links:ERC-8004: Trustless Agents
Disclaimer:I carefully examine and write the information that I research, but since it is personally operated and there are many parts with English sources, there may be some paraphrasing or incorrect information. Please understand. Also, there may be introductions of Dapps, NFTs, and tokens in the articles, but there is absolutely no solicitation purpose. Please purchase and use them at your own risk.
About us
🇯🇵🇺🇸🇰🇷🇨🇳🇪🇸 The English version of the web3 newsletter, which is available in 5 languages. Based on the concept of ``Learn more about web3 in 5 minutes a day,'' we deliver research articles five times a week, including explanations of popular web3 trends, project explanations, and introductions to the latest news.
Author
mitsui
A web3 researcher. Operating the newsletter "web3 Research" delivered in five languages around the world.
Contact
The author is a web3 researcher based in Japan. If you have a project that is interested in expanding to Japan, please contact the following:
Telegram:@mitsui0x
*Please note that this newsletter translates articles that are originally in Japanese. There may be translation mistakes such as mistranslations or paraphrasing, so please understand in advance.